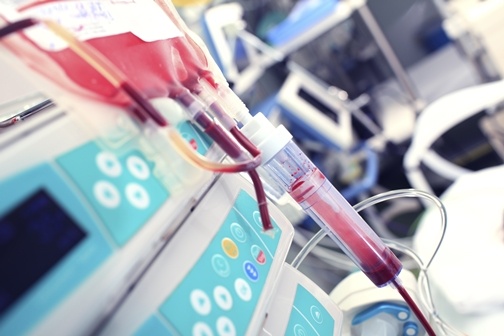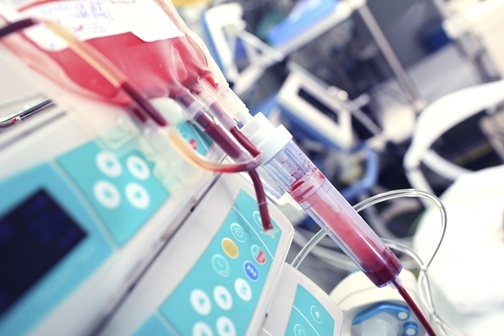
There are nearly 80 different medical treatments which involve the use of a cord blood stem cell transplant. All of these treatments involve the use of the hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that can be found in umbilical cord blood or within bone marrow (Cordblood.com, 2015). Some HSCs are also found in the bloodstream and are termed peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs).
Hematopoietic stem cells can divide to form more HSCs or they mature into three different types of blood cells:
- White blood cells which combat infections
- Red blood cells which carry oxygen
- Platelets which help the blood clot
The illnesses which can be treated with HSCs involve the depletion of a person’s ability to create blood cells either due to a disease, genetic condition or medical treatment like chemotherapy.
Transplanting HSCs can re-establish a person’s ability to produce healthy and functional blood cells, restoring immune function, clotting and the ability to carry sufficient levels of oxygen throughout a person’s body.
The Different Types of Stem Cell Transplants
Stem cells can be transplanted via bone marrow transplantation (BMT) or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT). The stem cells found in the cord blood are transplanted by PBSCT, a fairly quick procedure that does not involve surgery. The stem cells are given to the patient intravenously and migrate to the bone marrow.
The source for stem cell transplants can come from three sources (National Cancer Institute, 2015):
- Autologous transplants where the patient receives their own stem cells
- Syngeneic transplants where patients receive stem cells from their identical twin
- Allogeneic transplants, where patients receive stem cells from a close relative or unrelated person
The Process for Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplant
There are typically 5 steps involved between the time umbilical cord blood is gathered and used in a cord blood stem cell transplant.
1) Collection
The umbilical cord stem cells are collected after the baby has been born and umbilical cord has been clamped and cut. The cord blood is drained from the umbilical cord using a collection kit. The umbilical cord tissue can also be preserved as it contains valuable stem cells. The entire collection process usually takes between 15 and 20 minutes. It is painless and completely safe for both mother and child.
The cord blood and cord tissue are then placed in a cord blood shipping container and a courier delivers it to the laboratory.
2) Testing and Processing
The cord blood and cord tissue is tested to ensure that the stem cells are of sufficient quality and no infectious agents are present within the blood. A report is created which informs parents about the number of healthy stem cells preserved. At Cells4Life, we provide parents an official Testing Certificate that shows the complete results of processing the cord blood and cord tissue. Learn more about the Cells4Life cord blood banking in UAE.
The cord blood can be stored as whole cord blood (with limited processing) or it can be volume-reduced to make it easier to use for HSC transplantation. The advantage of storing whole cord blood is that all types of stem cells are preserved including Multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC), Very Small Embryonic-Like Stem Cells (VSELs) and Unrestricted Somatic Stem Cells (USSCs).
MSCs and VSELs are currently the subject of a great deal of research into regenerative medicine treatments which seek to cure previously untreatable illnesses and injuries. Many parents are opting to store whole cord blood to take advantage of possible medical breakthroughs in the future.
The main advantage of volume-reduction is that the sample is purified before freezing, so it is immediately ready for a cord blood stem cell transplant. It is frozen in its “ready-state”.
3) Freezing
The samples are then cryogenically frozen. Researchers have demonstrated that stem cells can remain viable for at least 23 years while in a cryogenically frozen state. Learn more about how long you can preserve your baby’s cord blood stem cells here.
4) Usage
When a transplant is required, the stem cells are thawed and prepared for transplantation.
5) Healing Process
After the stem cells have been infused into a patient they take approximately 24 hours to reach their destination. The cells begin to grow and multiply, enabling the patient to produce healthy and normal blood cells once again. The patient may have to be isolated while their immune system function is rebuilt using the new white blood cells.
Diseases that can be treated with Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplant
HSCs have been used to successfully treat many blood disorders, immune system disorders, metabolic disorders and blood cancers. HSCs are most commonly used to treat cancer because it can restore a person’s ability to produce healthy blood cells after chemotherapy has compromised it.
Some of the conditions which can be treated with HSCs include:
- Fanconi Anemia
- Pure Red Cell Aplasia
- Acute Myelofibrosis
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
- Ewing Sarcoma
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Congenital Neutropenia
- Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria (Gunther Disease)
- Hunter Syndrome (MPS-II) and Hurler Syndrome (MPS-IH)
- Neuroblastoma
- Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency (SCID)
The stem cells found in the cord blood have a proven track record for saving lives and as medical technologies advance, their use will only increase.
Sources:
Cordblood.com,. (2015). Stem Cell Treatment | Cord Blood Treatment | CBR®. Retrieved 2 August 2015, from http://www.cordblood.com/benefits-cord-blood/umbilical-cord-stem-cells/stem-cell-treatments
National Cancer Institute,. (2015). Blood-Forming Stem Cell Transplants. Retrieved 3 August 2015, from http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/stem-cell-transplant/stem-cell-fact-sheet#q1
*This article was first published in October 14, 2014.