Placenta Banking
Placenta banking gives your baby more therapeutic options throughout their entire life.
What is Placenta Banking?
Your placenta plays a vital role in the health of your baby as it grows in the womb. However, after you have given birth, the placenta can still provide support for your baby.
The placenta is also a rich source of valuable cells that have already been used to heal serious burns, as well as heal infected wounds. Clinical trials are also proving extremely promising when it comes to treating brain injury, arthritis, and cardiovascular conditions, to name a few.
To provide your family with the chance to benefit from the exciting possibilities of regenerative medicine, we offer the following placenta banking options:
- Placenta (maternal side)
- Amnion
- Chorionic Villi
For more information on placenta banking, read more or contact us today!
Watch Video to Learn More:

Powerful
The cells taken from the placenta are perinatal, which means they are younger and have greater regenerative potential.

Safe
Collecting cells from the placenta is a quick, simple, non-invasive and completely safe profess for the mother and baby.

Unique
Placenta cells are unique – they are a perfect match for your baby and can also be used by the mother to access regenerative therapies.
Chorionic Villi Storage
Cells4Life stores the placenta cells from the chorionic villi – the small, tree-like structures which extend outwards from the chorion.
The chorion is the outer membrane of the sac which holds your baby during your pregnancy.
As your baby develops, the chorionic villi maximise contact with mum’s blood stream to ensure they receive all the essential nutrients and cells they need to grow in the womb.
The chorionic villi are rich in regenerative cells. By opting for Chorionic Villi Storage, these cells can continue to support your baby’s health for years to come.

More cells, more treatments
- Storing placenta maximises the number of cells parents can store.
- It provides access to as many regenerative therapies as possible, as they become available.
- More cells stored could enable more treatments or mean the difference between treating a small child or a fully-grown adult.

The only placental bank in the UK
- Cells4Life is the only placenta storage bank that promises to isolate specific therapeutic cell types.
- We are also the only amnion bank – already used in therapy.
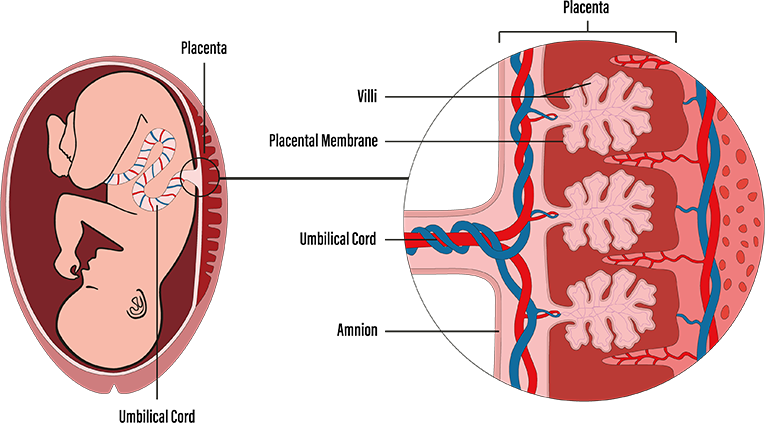
Amnion Storage
The amnion is the innermost layer of the placenta – also known as the amniotic membrane.
It begins as a sheath around the umbilical cord, which evolves during pregnancy into a thin lining of the placenta sac. Placenta tissue is particularly significant because it contains collagen, fibronectin and hyaluronic acid; these three components are linked with enhanced healing.
The amniotic membrane also contains a combination of growth factors and anti-inflammatory proteins, which can help cells communicate when the body is damaged or diseased. There is also evidence that placenta tissue is antimicrobial.

Protect the whole family
- Amnion is non-immunogenic – it can be used to treat unmatched patients: parents, siblings or other, more distant relatives.
- Amnion cells have been administered to babies with broncho-pulmonary dysplasia and found to be safe and well-tolerated.

More cells, more treatment
- Amnion has been used since 1910 to treat conditions like burns and wounds:
- 1910 – first documented amnion skin graft.
- 1913 – amnion was proven to be more effective at healing skin wounds than other methods.
- In the USA, disorders of the cornea account for 41% of all amnion transplants.
Placenta Banking with Cells4Life
Everything about our service has been designed to provide your baby and your family with the best long-term health protection possible. Here are just a few of the benefits of placenta banking with Cells4Life:
√ The UK’s only placenta collection service
√ More stem cells, more treatments
√ Multiple samples in two storage locations
√ Most comprehensive range of services
√ Processing lab open 24/7, 365 days a year
√ Industry-leading technology
√ Stem cell insurance
√ HTA licensed
√ AABB accredited
√ DHA-licensed facility in the UAE
How Does the Placenta Collection Work?
1. Sign Up with Cells4Life
Contact one of our Cells4Life representative to discuss about your options. Once you submitted the signed storage agreement, you will receive your collection kit.
4. Placenta Collection
Once your baby is born and the placenta is delivered, your doctor or midwife will proceed on the collection using the kit your provided.
2. Inform Your Doctor
It is important to inform your doctor, OB-GYN or midwife about your decision to collect the placenta to make sure that it will be done at the time of your delivery using the kit provided.
5. Contact Us
Once the placenta is packed properly in the collection kit, call us and we will arrange for the sample pick up and shipment to the UK lab for processing.
3. Bring Kit to the Hospital
At the time of your birth, make sure to bring your collection kit with you to the hospital. You can put it beside the other important things you will bring to the hospital.
6. Processing & Results
The harvested placenta cell samples will undergo testing and processing as soon as they are received at the lab and initial results will be sent between 2-5 days.
Placenta Cells: Clinical Trials

Ischaemic stroke
Scientists have used stem cells from the amnion to create functional muscles, jawbone fragments and even ears using 3D printers.

Diabetes
After receiving cells from the placenta, patients with Type 2 diabetes experienced increased levels of insulin and 4 out of 10 patients reduced their insulin doses by more than 50%.

Crohn’s disease
Preclinical studies have used placenta cells from the chorionic villi to decrease inflammation in the liver, which is a symptom of Crohn’s disease.

Heart disease
Cells from the chorionic villi have are expected to help create heart valves, and maybe even replace blood vessels.

Osteoarthritis
Chinese researchers have injected placenta cells into arthritic knees to determine if they can reduce inflammation, stiffness, pain and loss of movement.
Amnion: Proven Uses

Ulcers
Amnion can induce ‘epithelialisation’, the process where the body replaces skin cells in a wound. One study found wounds healed by 92% within 6 weeks vs 8% using standard of care.

Burns
Since 1910, amnion has been used for skin grafts and in 2017, researchers found it can induce ‘epithelialisation’ where the body replaces damaged skin cells.

Eyes
Amnion has been used since the 1990s in ophthalmology to reduce pain and inflammation in various eye conditions.
Amnion: Clinical Trials

Diabetes
A study in 2016 showed an amnion injection of placenta tissue-derived cells might be able to improve glycaemic control in patients with diabetes.

Dry eye
Doctors have used amnion to enhance recovery in 90 patients with severe dry eye and saw an improvement in 88% of cases.

3D printing body parts
Scientists have used stem cells from the amnion to create functional muscles, jawbone fragments and even ears using 3D printers.

Cardiovascular conditions
Patches of the amniotic membrane have been used to treat patients with inflammatory cardiovascular conditions.

Brain injury
Amnion-derived cells could help with brain injury by reprogramming inflammatory responses, and permanently improving neurological function.
References:
- B. Weber, S. M. Zeisberger, and S. P. Hoerstrup, “Prenatally harvested cells for cardiovascular tissue engineering: fabrication of autologous implants prior to birth,” Placenta, vol. 32, Supplement 4, pp. S316–S319, 2011.
- D. Schmidt, A. Mol, C. Breymann et al., “Living autologous heart valves engineered from human prenatally harvested progenitors,” ells in type 2 diabetes: a pilot study.” Front Med. 2011 Mar;5(1):94-100. doi: 10.1007/s11684-011-0116-z. Epub 2011 Mar 17.
- Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH, et al. Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2011;42:2045–2053
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28413063
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5426882/
- https://www.england.nhs.uk/north/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2018/05/NWCSN_Diabetes_Footcare_Final_Report_2017-1.pdf
- Fetterolf D, Snyder R. Scientific and Clinical Support for the Use of Dehydrated Amniotic Membrane in Wound Management. Wounds. 2012;24(10):299-307.
- Zelen C, Serena T. Amniotic Membrane: Can it facilitate healing? Podiatry Today. 2015 Apr;28(4). Available at http://www.podiatrytoday.com/amniotic-membrane-can-it-facilitate-healing
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5898584/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5270242/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20719087
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5845510/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6434489/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27735027




